|
RTI Connext Modern C++ API
Version 6.0.1
|
|
RTI Connext Modern C++ API
Version 6.0.1
|
Configurable IPv6/UDP Transport-Plugin properties. More...
Public Attributes | |
| struct NDDS_Transport_Property_t | parent |
| Generic properties of all transport plugins. | |
| RTI_INT32 | send_socket_buffer_size |
| Size in bytes of the send buffer of a socket used for sending. | |
| RTI_INT32 | recv_socket_buffer_size |
| Size in bytes of the receive buffer of a socket used for receiving. | |
| RTI_INT32 | unicast_enabled |
| Allows the transport plugin to use unicast for sending and receiving. | |
| RTI_INT32 | multicast_enabled |
| Allows the transport plugin to use multicast for sending and receiving. | |
| RTI_INT32 | multicast_ttl |
| Value for the time-to-live parameter for all multicast sends using this plugin. | |
| RTI_INT32 | multicast_loopback_disabled |
| Prevents the transport plugin from putting multicast packets onto the loopback interface. | |
| RTI_INT32 | ignore_loopback_interface |
| Prevents the transport plugin from using the IP loopback interface. | |
| RTI_INT32 | ignore_nonrunning_interfaces |
| Prevents the transport plugin from using a network interface that is not reported as RUNNING by the operating system. | |
| RTI_INT32 | no_zero_copy |
| [DEPRECATED] Prevents the transport plugin from doing zero copy. | |
| RTI_INT32 | send_blocking |
| Control blocking behavior of send sockets. CHANGING THIS FROM THE DEFAULT CAN CAUSE SIGNIFICANT PERFORMANCE PROBLEMS. | |
| RTI_INT32 | enable_v4mapped |
| Specify whether UDPv6 transport will process IPv4 addresses. | |
| RTI_UINT32 | transport_priority_mask |
| Set mask for use of transport priority field. | |
| RTI_INT32 | transport_priority_mapping_low |
| Set low value of output range to IPv6 TCLASS. | |
| RTI_INT32 | transport_priority_mapping_high |
| Set high value of output range to IPv6 TCLASS. | |
| RTI_INT32 | send_ping |
| Configures whether to send PING messages. | |
| RTI_INT32 | force_interface_poll_detection |
| Forces the interface tracker to use a polling mechanism to detect changes on the UDPv6 interfaces. | |
| RTI_UINT32 | interface_poll_period |
| Specifies the period in milliseconds to query for changes in the state of all the interfaces. | |
| RTI_INT32 | reuse_multicast_receive_resource |
| Controls whether or not to reuse multicast receive resources. | |
| RTI_INT32 | protocol_overhead_max |
| Maximum size in bytes of protocol overhead, including headers. | |
| RTI_INT32 | disable_interface_tracking |
| Disables detection of network interface changes. | |
| RTI_UINT32 | join_multicast_group_timeout |
| [Windows only] Defines how much time (milliseconds) to wait to join a multicast group address when a new interface is detected. | |
| char * | public_address |
| Public IP address associated with the transport instantiation. | |
Configurable IPv6/UDP Transport-Plugin properties.
The properties in this structure can be modified by the end user to configure the plugin. However, the properties must be set before the plugin is instantiated.
| struct NDDS_Transport_Property_t NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::parent |
Generic properties of all transport plugins.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::send_socket_buffer_size |
Size in bytes of the send buffer of a socket used for sending.
On most operating systems, setsockopt() will be called to set the SENDBUF to the value of this parameter.
This value must be greater than or equal to Transport_Property_t::message_size_max. The maximum value is operating system-dependent.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::recv_socket_buffer_size |
Size in bytes of the receive buffer of a socket used for receiving.
On most operating systems, setsockopt() will be called to set the RECVBUF to the value of this parameter.
This value must be greater than or equal to Transport_Property_t::message_size_max. The maximum value is operating system-dependent.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::unicast_enabled |
Allows the transport plugin to use unicast for sending and receiving.
This value turns unicast UDP on (if set to 1) or off (if set to 0) for this plugin. By default, it will be turned on (1). Also by default, the plugin will use all the allowed network interfaces that it finds up and running when the plugin is instanced.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::multicast_enabled |
Allows the transport plugin to use multicast for sending and receiving.
This value turns multicast UDP on (if set to 1) or off (if set to 0) for this plugin. By default, it will be turned on (1) for those platforms that support multicast. Also by default, the plugin will use the all network interfaces allowed for multicast that it finds up and running when the plugin is instanced.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::multicast_ttl |
Value for the time-to-live parameter for all multicast sends using this plugin.
This is used to set the TTL of multicast packets sent by this transport plugin.
[default] 1
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::multicast_loopback_disabled |
Prevents the transport plugin from putting multicast packets onto the loopback interface.
If multicast loopback is disabled (this value is set to 1), then when sending multicast packets, RTI Connext will not put a copy of the packets on the loopback interface. This prevents applications on the same node (including itself) from receiving those packets.
This value is set to 0 by default, meaning multicast loopback is enabled.
Disabling multicast loopback (setting this value to 1) may result in minor performance gains when using multicast.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::ignore_loopback_interface |
Prevents the transport plugin from using the IP loopback interface.
Currently three values are allowed:
The current "automatic" (-1) RTI Connext policy is as follows.
[default] -1 Automatic RTI Connext policy based on availability of the shared memory transport.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::ignore_nonrunning_interfaces |
Prevents the transport plugin from using a network interface that is not reported as RUNNING by the operating system.
The transport checks the flags reported by the operating system for each network interface upon initialization. An interface which is not reported as UP will not be used. This property allows the same check to be extended to the IFF_RUNNING flag implemented by some operating systems. The RUNNING flag is defined to mean that "all resources are allocated", and may be off if there is no link detected, e.g., the network cable is unplugged.
Two values are allowed:
[default] 1 (i.e., check RUNNING flag)
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::no_zero_copy |
[DEPRECATED] Prevents the transport plugin from doing zero copy.
DEPRECATED: This property has no effect. By default, this plugin will use the zero copy on OSs that offer it. While this is good for performance, it may sometimes tax the OS resources in a manner that cannot be overcome by the application.
The best example is if the hardware/device driver lends the buffer to the application itself. If the application does not return the loaned buffers soon enough, the node may error or malfunction. If you cannot reconfigure the H/W, device driver, or the OS to allow the zero copy feature to work for your application, you may have no choice but to turn off the use of zero copy.
By default this is set to 0, so RTI Connext will use the zero copy API if offered by the OS.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::send_blocking |
Control blocking behavior of send sockets. CHANGING THIS FROM THE DEFAULT CAN CAUSE SIGNIFICANT PERFORMANCE PROBLEMS.
Currently two values are defined:
[default] NDDS_TRANSPORT_UDPV6_BLOCKING_ALWAYS.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::enable_v4mapped |
Specify whether UDPv6 transport will process IPv4 addresses.
Set this to 1 to turn on processing of IPv4 addresses. Note that this may make it incompatible with use of the UDPv4 transport within the same domain participant.
[default] 0.
| RTI_UINT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::transport_priority_mask |
Set mask for use of transport priority field.
If transport priority mapping is supported on the platform, this mask is used in conjunction with UDPv6Transport_Property_t::transport_priority_mapping_low and UDPv6Transport_Property_t::transport_priority_mapping_high to define the mapping from DDS transport priority (see TRANSPORT_PRIORITY) to the IPv6 TCLASS field. Defines a contiguous region of bits in the 32-bit transport priority value that is used to generate values for the IPv6 TCLASS field on an outgoing socket. (See the Getting Started Guide to find out if the transport priority is supported on a specific platform.)
For example, the value 0x0000ff00 causes bits 9-16 (8 bits) to be used in the mapping. The value will be scaled from the mask range (0x0000 - 0xff00 in this case) to the range specified by low and high.
If the mask is set to zero, then the transport will not set IPv6 TCLASS for send sockets.
[default] 0.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::transport_priority_mapping_low |
Set low value of output range to IPv6 TCLASS.
This is used in conjunction with UDPv6Transport_Property_t::transport_priority_mask and UDPv6Transport_Property_t::transport_priority_mapping_high to define the mapping from DDS transport priority to the IPv6 TCLASS field. Defines the low value of the output range for scaling.
Note that IPv6 TCLASS is generally an 8-bit value.
[default] 0.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::transport_priority_mapping_high |
Set high value of output range to IPv6 TCLASS.
This is used in conjunction with UDPv6Transport_Property_t::transport_priority_mask and UDPv6Transport_Property_t::transport_priority_mapping_low to define the mapping from DDS transport priority to the IPv6 TCLASS field. Defines the high value of the output range for scaling.
Note that IPv6 TCLASS is generally an 8-bit value.
[default] 0xff.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::send_ping |
Configures whether to send PING messages.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::force_interface_poll_detection |
Forces the interface tracker to use a polling mechanism to detect changes on the UDPv6 interfaces.
| RTI_UINT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::interface_poll_period |
Specifies the period in milliseconds to query for changes in the state of all the interfaces.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::reuse_multicast_receive_resource |
Controls whether or not to reuse multicast receive resources.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::protocol_overhead_max |
Maximum size in bytes of protocol overhead, including headers.
This value is the maximum size, in bytes, of protocol-related overhead. Normally, the overhead accounts for UDP and IP headers. The default value is set to accommodate the most common UDP/IP header size.
Note that when Transport_Property_t::message_size_max plus this overhead is larger than the UDPv6 maximum message size (65535 bytes), the middleware will automatically reduce the effective message_size_max, to 65535 minus this overhead.
[default] 48.
| RTI_INT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::disable_interface_tracking |
Disables detection of network interface changes.
| RTI_UINT32 NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::join_multicast_group_timeout |
[Windows only] Defines how much time (milliseconds) to wait to join a multicast group address when a new interface is detected.
| char* NDDS_Transport_UDPv6_Property_t::public_address |
Public IP address associated with the transport instantiation.
Setting the public IP address is only necessary to support communication over WAN that involves Network Address Translation (NAT).
Typically, the address is the public address of the IP NAT router that provides access to the WAN.
By default, the dds::domain::DomainParticipant creating the transport will announce the IP addresses obtained from the NICs to other DomainParticipants in the system.
When this property is set, the DomainParticipant will announce the IP address corresponding to the property value instead of the LAN IP addresses associated with the NICs.
Note 1: Setting this property is necessary, but is not a sufficient condition for sending and receiving data over the WAN. You must also configure the IP NAT router to allow UDP traffic and to map the public IP address specified by this property to the DomainParticipant's private LAN IP address. This is typically done with one of the following mechanisms:
Port Forwarding: You must map the private ports used to receive discovery and user data traffic to the corresponding public ports (see rti::core::RtpsWellKnownPorts). Public and private ports must be the same since the transport does not allow you to change the mapping.
Note 2: By setting this property, the dds::domain::DomainParticipant only announces its public IP address to other DomainParticipants. Therefore, communication with DomainParticipants within the LAN that are running on different nodes will not work unless the NAT router is configured to enable NAT reflection (hairpin NAT).
There is another way to achieve simultaneous communication with DomainParticipants running in the LAN and WAN, that does not require hairpin NAT. This way uses a gateway application such as RTI Routing Service to provide access to the WAN.
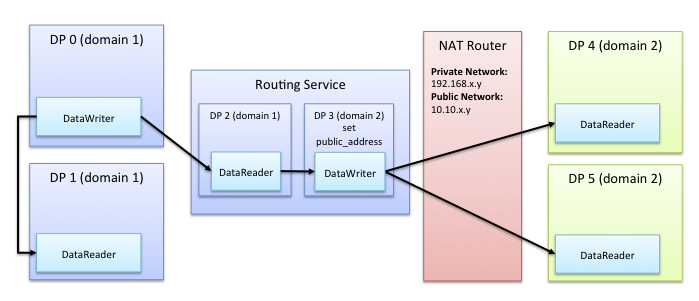
[default] null (the transport uses the IP addresses obtained from the NICs)