8.6.6 TYPE_CONSISTENCY_ENFORCEMENT QosPolicy
The TypeConsistencyEnforcementQosPolicy defines the rules that determine whether the type used to publish a given topic is consistent with the type used to subscribe to it.
The QosPolicy structure includes the members in the following table.
|
Type |
Field Name |
Description |
|
DDS_TypeConsistencyKind |
kind |
Can be any of the following values:
See below for details. |
|
DDS_Boolean |
ignore_sequence_bounds |
Controls whether sequence bounds are taken into consideration for type assignability. If false, a sequence with a larger maximum length may not be assigned to a sequence with a smaller maximum length. If true, sequences and strings in a DataReader type can have a maximum length smaller than that of the DataWriter type. When the length of the sequence in a particular sample is larger than the maximum length, that sample is discarded. Default: false |
|
DDS_Boolean |
ignore_string_bounds |
Controls whether string bounds are taken into consideration for type assignability. If false, then a string with a larger maximum length may not be assigned to a string with a smaller maximum length. Default: false. |
|
DDS_Boolean |
ignore_member_names |
Controls whether member names are taken into consideration for type assignability. If false, members with the same ID and different names are not assignable to each other. If true, members of a type can change their name while keeping their member ID. For example, MyType and MyTypeSpanish are only assignable if ignore_member_names is true: struct MyType {@id(10) int32 x; @id(20) int32 angle; }; struct MyTypeSpanish {@id(10) int32 x; @id(20) int32 angulo; }; Default: false |
|
DDS_Boolean |
prevent_type_widening |
Controls whether type widening is allowed. A type T2 widens a type T1 when T2 contains required members that are not present in T1. If a DataReader of T2 sets prevent_type_widening to true, then the DataReader will not be matched with a DataWriter of T1 because T1 is not assignable to T2. Default: false |
|
DDS_Boolean |
force_type_validation |
Controls whether type information must be available in order to complete matching between a DataWriter and this DataReader. If false, matching may occur as long as the type names match. Note that if the types have the same name but are not assignable, DataReaders may fail to deserialize incoming data samples. Default: false |
|
DDS_Boolean |
ignore_enum_literal_names |
Controls whether enumeration constant names are taken into consideration for type assignability. If the option is set to true, then enumeration constants may change their names, but not their values, and still maintain assignability. If the option is set to false, then in order for enumerations to be assignable, any constant that has the same value in both enumerations must also have the same name. For example, enum Color {RED = 0} and enum Color {ROJO = 0} are assignable if and only if ignore_enum_literal_names is true. Default: false |
The type-consistency enforcement rules consist of two steps:
- If both the DataWriter and DataReader specify a TypeObject, it is considered first. If the DataReader allows type coercion, then its type must be assignable from the DataWriter’s type, taking into account the values of prevent_type_widening, ignore_sequence_bounds, ignore_string_bounds, ignore_member_names, and ignore_enum_literal_names. If the DataReader does not allow type coercion, then its type must be equivalent to the type of the DataWriter.
- If either the DataWriter or the DataReader does not provide a TypeObject definition, then the registered type names are examined. The DataReader’s and DataWriter’s registered type names must match exactly, as was true in Connext DDS releases prior to 5.0. This step will fail if force_type_validation is true, regardless of the type names.
If either Step 1 or Step 2 fails, the Topics associated with the DataReader and DataWriter are considered to be inconsistent and the 5.3.1 INCONSISTENT_TOPIC Status is updated.
The default enforcement kind is DDS_AUTO_TYPE_COERCION. This default kind translates to DDS_ALLOW_TYPE_COERCION, except in the following cases:
- When a Zero Copy DataReader is used, the kind is translated to DDS_DISALLOW_TYPE_COERCION.
- When the middleware is introspecting the built-in topic data declaration of a remote DataReader in order to determine whether it can match with a local DataWriter, if it observes that no TypeConsistencyEnforcementQosPolicy value is provided (as would be the case when communicating with a Service implementation not in conformance with this specification), it assumes a kind of DDS_DISALLOW_TYPE_COERCION.
8.6.6.1 Values for TypeConsistencyKind
- AUTO_TYPE_COERCION (default)
For a regular DataReader, this default value is translated to ALLOW_TYPE_COERCION. For a Zero Copy DataReader, this default value is translated to DISALLOW_TYPE_COERCION. (See 23.5 Zero Copy Transfer Over Shared Memory for information on why a Zero Copy DataReader requires the DISALLOW_TYPE_COERCION option.)
- DISALLOW_TYPE_COERCION
- ALLOW_TYPE_COERCION
With this setting, the DataWriter and DataReader must support the same data type in order for them to communicate. (This is the degree of enforcement required by the OMG DDS Specification prior to the OMG ‘Extensible and Dynamic Topic Types for DDS’ specification.)
When Connext DDS is introspecting the built-in topic data declaration of a remote DataWriter or DataReader, if no TypeConsistencyEnforcementQosPolicy value is provided (as would be the case when communicating with an implementation not in conformance with the Extensible and Dynamic Topic Types for DDS" (DDS-XTypes) specification), Connext DDS shall assume a kind of DISALLOW_TYPE_COERCION.
With this setting, the DataWriter and the DataReader need not support the same data type in order for them to communicate, as long as the DataReader’s type is assignable from the DataWriter’s type.
For example, the following two extensible types will be assignable to each other since MyDerivedType contains all the members of MyBaseType (member_1) plus an additional element (member_2).
struct MyBaseType {
long member_1;
};
struct MyDerivedType: MyBaseType {
long member_2;
};
Even if MyDerivedType was not explicitly inherited from MyBaseType, the types would still be assignable. For example:
struct MyBaseType {
long member_1;
};
struct MyDerivedType {
long member_1;
long member_2;
};
For more information, see the RTI Connext DDS Core Libraries Getting Started Guide Addendum for Extensible Types and the OMG ‘Extensible and Dynamic Topic Types for DDS’ Specification.
8.6.6.2 Prevent Type Widening
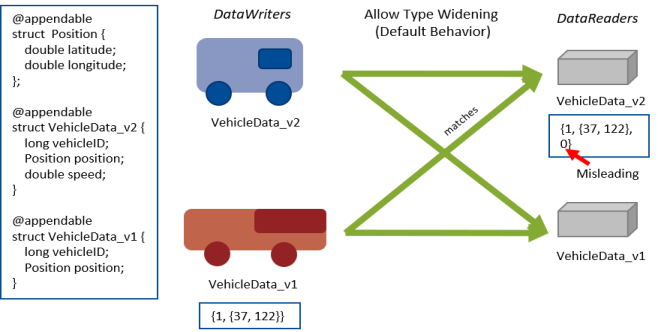
The prevent_type_widening field determines whether type widening is allowed. In Figure 8.25: prevent_type_widening = false, VehicleData_v2 has three members and VehicleData_v1 two members. With type widening allowed, the narrower car (VehicleData_v1, with two members) can write to the wider car (VehicleData_v2), but notice that the DataReader assumes a value that might be misleading (in this case, a default speed of zero).
Figure 8.25: prevent_type_widening = false
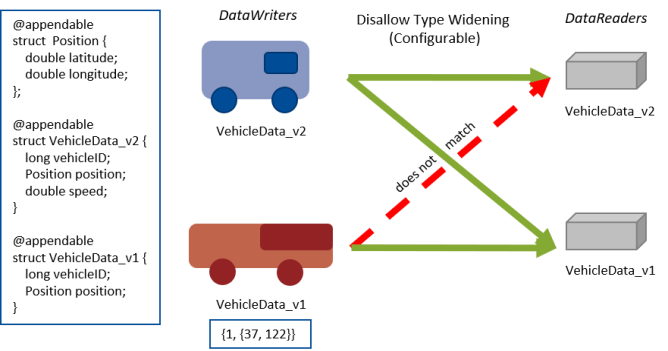
If widening is not allowed (Figure 8.26: prevent_type_widening = true), VehicleData_v1 and VehicleData_v2 do not communicate with each other.
Figure 8.26: prevent_type_widening = true
8.6.6.3 Properties
This QosPolicy cannot be modified after the DataReader is enabled.
It only applies to DataReaders, so there is no requirement that the publishing and subscribing sides use compatible values.
8.6.6.4 Related QoS Policies
- None.
8.6.6.5 Applicable Entities
8.6.6.6 System Resource Considerations
- None.
© 2020 RTI
