6. Configuration¶
6.1. Configuring Cloud Discovery Service¶
This section provides a reference for the XML elements that conform a Routing Service configuration. For details on how to provide XML configurations to Routing Service. refer to Configuring RTI Services. This chapter describes how to write an XML configuration.
6.2. XML Tags for Configuring RTI Cloud Discovery Service¶
This section describes the XML tags you can use in a Cloud Discovery Service configuration file.
The following diagram and Table 6.1 describe the top-level
tags allowed within the root <dds> tag.

Figure 6.1 Top-level Tags in the Configuration File¶
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Specifies a Cloud Discovery Service configuration.
|
1..*. |
6.2.1. Cloud Discovery Service¶
A configuration file must have at least one <cloud_discovery_service>
tag. This tag is used to configure an execution of Cloud Discovery Service. A configuration file
may contain multiple <cloud_discovery_service> tags.
When you start Cloud Discovery Service, you can specify which <cloud_discovery_service> tag
to use to configure the service using the -cfgName command-line option.
Because a configuration file may contain multiple <cloud_discovery_service>
tags, one file can be used to configure multiple Cloud Discovery Service executions.
Figure 6.2 and
Table 6.2 describe the tags allowed within a
<cloud_discovery_service> tag.
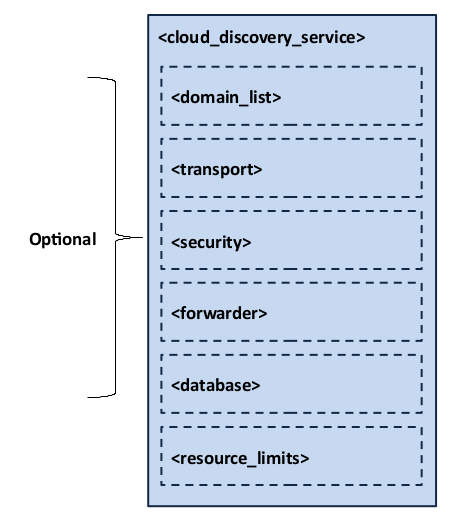
Figure 6.2 Cloud Discovery Service Tag Structure¶
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Enables remote administration. When administration is enabled, monitoring is also enabled by default. If no domain ID is specified for monitoring, Cloud Discovery Service will use the same domain as administration by default. See Administration. |
0..1 |
|
Enables monitoring for Cloud Discovery Service, including the periodic publication of statistics. See Section 6.2.3. |
0..1 |
|
Set of domains for which the service forwards participant
announcements. |
0..1 |
|
Selection of unicast transport resources where the service receives
and sends participant announcements. |
0..1 |
|
Configures the security features provided by the RTI Security Plugins. |
0..1 |
|
Configures the behavior of the participant announcement forwarding
logic. |
0..1 |
|
Configures the behavior of the service’s internal database,
which contains information about the discovery state. |
0..1 |
|
Service resource management policies. |
0..1 |
6.2.1.1. Example: Specify a Configuration in XML¶
<dds>
<cloud_discovery_service name="EmptyConfiguration"/>
<cloud_discovery_service name="ShapesDemoConfiguration">
<!--...-->
</cloud_discovery_service>
</dds>
Starting Cloud Discovery Service with the following command will use the
<cloud_discovery_service> tag with the name EmptyConfiguration.
$NDDSHOME/bin/rticlouddiscoveryservice \
-cfgFile file.xml -cfgName EmptyConfiguration
6.2.2. Administration¶
The <administration> tag allows you to enable and configure remote
administration of Cloud Discovery Service, including stopping, starting, and deleting a Cloud Discovery Service
instance.
See Remote Administration for details on using remote administration.
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Domain ID used for remote administration. Also used for monitoring by default. |
0..1 |
|
QoS used by the administration DomainParticipant. If the tag is not defined, Connext DDS defaults will be used. |
0..1 |
|
QoS used by the administration Publisher. If the tag is not defined, Connext DDS defaults will be used. |
0..1 |
|
QoS used by the administration Subscriber. If the tag is not defined, Connext DDS defaults will be used. |
0..1 |
|
QoS used by administration DataWriter(s). If the tag is not defined, Connext DDS defaults will be used, with the following changes:
|
0..1 |
|
Quality of Service (QoS) used by administration DataReader(s). If the tag is not defined, the Connext DDS defaults will be used, with the following changes:
|
0..1 |
|
When you enable Distributed Logger, Cloud Discovery Service will publish its log messages to Connext DDS. See Enabling Distributed Logger. |
0..1 |
The contents of the tags for configuring QoS are specified in the same manner as for the Connext DDS XML QoS Profiles file. See Configuring QoS with XML, in the RTI Connext DDS Core Libraries User’s Manual.
6.2.3. Monitoring¶
The <monitoring> tag allows you to enable and configure remote
monitoring of Cloud Discovery Service.
See Monitoring.
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Whether to enable monitoring of the service. Default: Disabled, unless administration is enabled. |
0..1 |
|
Domain ID used for monitoring. Default: The domain ID specified for monitoring. |
0..1 |
|
QoS used by monitoring DataWriter(s) |
0..1 |
|
QoS used by monitoring Publisher(s) |
0..1 |
|
QoS used by monitoring DomainParticipant |
0..1 |
|
How frequently to sample the service’s statistics, using the tags <sec> and <nanosec>. For example, <sec>1</sec> samples the service’s statistics every second. |
0..1 |
|
How frequently to publish the service status, using the tags <sec> and <nanosec>. For example, <sec>1</sec> publishes the service’s status every second. |
0..1 |
The contents of the tags for configuring QoS are specified in the same manner as for the Connext DDS XML QoS Profiles file. See Configuring QoS with XML, in the RTI Connext DDS Core Libraries User’s Manual.
6.2.4. Domain List¶
A <domain_list> allows you to control for which domains the discovery traffic
is propagated. Table 6.5 describes the tags allowed.
Figure 6.3 and
Table 6.5 describe the tags allowed within a
<domain_list> tag.

Figure 6.3 Domain List Tag Structure¶
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Set of domain IDs where the service forwards participant announcements.
|
0..1 |
|
Subset of the allowed domain IDs for which the service ignores
announcements. |
0..1 |
The <allow_domain_id> and <deny_domain_id> filters both allow the same
syntax, in which a subset of domains can be specified as a comma-separated list
containing one or more of the following elements:
Individual domains:
5, 6, 7Domain Range:
[1 - 10]- Special values:
DOMAIN_LIST_ALL: specifies all the available domains.(empty string): specifies none of the domains.
6.2.4.1. Example: Deny a Few Specific Domains¶
<domain_list>
<allow_domain_id>DOMAIN_LIST_ALL</allow_domain_id>
<deny_domain_id>5,7,10</deny_domain_id>
</domain_list>
6.2.4.2. Example: Allow a Subset of Domains¶
<domain_list>
<allow_domain_id>[10 - 30], 40, [50 - 100]</allow_domain_id>
</domain_list>
6.2.5. Transport¶
The <transport> element allows you to select and configure the resources used
to receive and send discovery traffic. A receive resource is uniquely
specified by a transport class-receive port pair. For each different transport
instance specified, Cloud Discovery Service creates a send resource.
Figure 6.4 and Table 6.6 shows the description of this element.
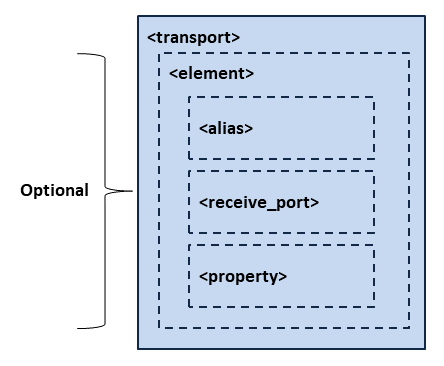
Figure 6.4 Transport Tag Structure¶
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Individual transport receive resource. |
0..* |
Each <element> within <transport> is a transport unicast receive
resource, specified by a transport alias and a receive port.
Table 6.7 describes the tags allowed.
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Identifies a concrete transport class instantiation. Note If you attempt to reuse a transport instance of a class that does not support reuse, Cloud Discovery Service will log a warning and continue loading. |
0..1 |
|
Port that the service listens on to receive participant announcements.
|
0..1 |
|
A sequence of name-value string pairs that allows configuring the underlying transport instance.
|
0..1 |
Cloud Discovery Service comes with the following preconfigured transport instances, which you can use and configure directly.
Note
You can override any of the preset transport properties. In such a case, Cloud Discovery Service will log a warning.
Alias |
Description |
Prefix |
|---|---|---|
|
Builtin implementation of UDPv4.
|
|
|
Implementation of UDPv4 for WAN networks.
Note Your library path requires libraries from RTI Real-Time WAN Transport Support
( |
|
|
Builtin implementation of UDPv6.
|
|
|
Implementation of TCPv4 for LAN and WAN networks.
Note Your library path requires libraries from RTI TCP Support
( |
|
6.2.5.1. Preregistered UDP Transports¶
Cloud Discovery Service registers an instance for the following UDP transports:
UDPv4
UDPv4 WAN or the RTI Real-Time WAN Transport
UDPv6
There are no preset properties for any of these instances.
See the following links for properties for each of these UDP transports respectively:
6.2.5.2. Preregistered TCP Transport¶
Cloud Discovery Service registers an instance of the RTI TCP transport. Table 6.9 shows a list of preset properties.
See RTI TCP Transport configuration for a list of available properties.
Property name (prefix with |
Property value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
The value of the corresponding |
|
|
6.2.5.3. Example: Reusing UDP Transport Instance for Multiple Receive Resources¶
<transport>
<element>
<alias>udpv4</alias>
<receive_port>7400</receive_port>
</element>
<element>
<alias>udpv4</alias>
<receive_port>7500</receive_port>
</element>
</transport>
6.2.5.4. Example: A Receive Resource for Each UDP and TCP Transport¶
This example shows how to specify different receive resources from different
transport instances. Additionally, it shows how to extend the behavior
of the preregistered TCP transport through the specification of additional
transport properties using the transport prefix dds.transport.cds.tcp1.
<transport>
<element>
<alias>builtin.UDPv4</alias>
<receive_port>7400</receive_port>
</element>
<element>
<alias>tcpv4_wan</alias>
<receive_port>8400</receive_port>
<property>
<element>
<name>dds.transport.cds.tcp1.tcp1.public_address</name>
<value>35.6.9.10</value>
</element>
</property>
</element>
</transport>
6.2.6. Security¶
The <security> element allows you to enable and configure the security
features provided by the Security Plugins. For further details, see Security.
Table 6.10 shows the description of this element.
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
A sequence of name-value string pairs that allows configuring security. These are the valid properties you can configure within this tag:
For further details, see Security.
|
0..1 |
6.2.7. Forwarder¶
The <forwarder> element allows you to configure the attributes and behavior
of the active component involved in the participant announcement forwarding
process.
Figure 6.5 and Table 6.11 describe this element.

Figure 6.5 Forwarder Tag Structure¶
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Configures the timing and behavior of forwarding repeating events. Elements:
|
0..1 |
|
Configures the pool of threads dedicated to the forwarding process.
|
0..1 |
|
Configures the announcement scheduling policy and the output traffic control. See Figure 6.6 and Table 6.12. |
0..1 |
The <flow_controller> element allows you to configure the output traffic
of Cloud Discovery Service. With the flow controller, you can limit the output capacity, assign
more of the output capacity to certain participant announcements, and also
throttle the output traffic.
Figure 6.6 and Table 6.12 describe this element.

Figure 6.6 Flow Controller Tag Structure¶
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Specifies a limit for the output capacity in jobs per second. |
0..1 |
|
Maximum amount of announcement jobs that can be dispatched at once. |
0..1 |
|
Configures the output capacity distribution depending on the participant announcement class. See Table 6.13.
|
0..1 |
|
Configures the maximum period at which the forwarder will attempt to
send pending announcements.
|
0..1 |
Note
Configuring only one flow controller parameter in isolation may result in inaccurate performance of the forwarder. It is recommended to configure all the flow controller parameters, to guarantee the expected behavior.
The <output_capacity_allocation> allows you to distribute the output
capacity to each participant announcement class. Each class element is an
integer that represents the percentage of the total output capacity used to
forward announcements of such class.
Table 6.13 describes this element.
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Percentage of the maximum output capacity dedicated to the new
participant announcement class. |
0..1 |
|
Percentage of the maximum output capacity dedicated to the update
participant announcement class. |
0..1 |
|
Percentage of the maximum output capacity dedicated to the refresh
participant announcement class. |
0..1 |
Note that the sum of the percentages from the three classes can never be greater than 100. Otherwise Cloud Discovery Service will log an error message and fail to start. Unless default values are used, if the allocation for one or more classes are not specified, Cloud Discovery Service will equally split the remaining of the output capacity among them.
6.2.7.1. Example: Flow Controller¶
This example shows how to set up a flow controller with a maximum output capacity of 5000 jobs/s, of which half is reserved only for new participant announcements, and the other half is equally distributed among the update and refresh classes (25/25).
<flow_controller>
<output_capacity>5000</output_capacity>
<output_capacity_allocation>
<new>50</new>
</output_capacity_allocation>
</flow_controller>
6.2.8. Database¶
The <database> element allows you to configure the behavior of the internal
database that contains the information that represents the discovery state of
the system.
Figure 6.7 and Table 6.14 describe this element.
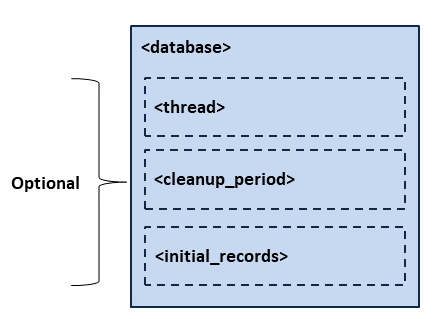
Figure 6.7 Database Tag Structure¶
Relevant tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Database thread settings. |
0..1 |
|
The period at which the service database thread wakes up to clean up
expired information.
|
0..1 |
|
The initial number of total records. |
0..1 |
6.2.9. Resource Limits¶
The <resource_limits> element allows you to specify upper limits of
memory consumption. In general, Cloud Discovery Service incorporates mechanisms to clean up unused
memory and maintain the execution within bounds when possible. Nevertheless,
you may need to tune the memory usage if you have special memory requirements.
Figure 6.8 and Table 6.15 describe this element.
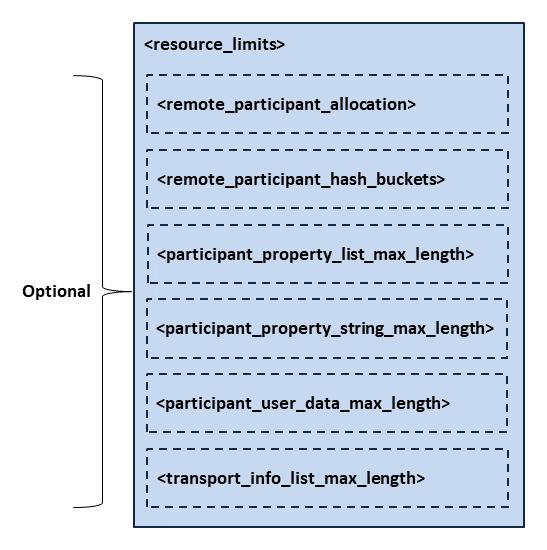
Figure 6.8 Resource Limits Tag Structure¶
Tags within |
Description |
Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
|
Allocation settings applied to remote DomainParticipants. |
0..1 |
|
Number of hash buckets for remote DomainParticipants. |
0..1 |
|
Maximum number of properties associated with the DomainParticipant. |
0..1 |
|
Maximum string length of the properties associated with the
DomainParticipant. |
0..1 |
|
Maximum length of user data to send and receive in a participant
announcement. |
0..1 |
|
Maximum number of installed transports to send and receive information
about a participant announcement. |
0..1 |
6.2.10. Enabling Distributed Logger¶
Distributed Logger is included in Connext DDS but it is not supported on all platforms; see the RTI Connext DDS Core Libraries Platform Notes for the set of platforms that support Distributed Logger.
When you enable Distributed Logger, the Cloud Discovery Service will publish its log messages to Connext DDS. Then you can use RTI Admin Console to visualize the log message data. Since the data is provided in a topic, you can also use rtiddsspy or even write your own visualization tool.
To enable Distributed Logger, use the tag <distributed_logger> within
<adminstration>. For example:
<cloud_discovery_service name="MyCDS"> <administration> ... <distributed_logger> <enabled>true</enabled> </distributed_logger> </administration> ... </cloud_discovery_service>
For more details, see Enabling Distributed Logger in RTI Services, in the RTI Connext DDS Core Libraries User’s Manual.
6.3. Builtin Configuration¶
Cloud Discovery Service comes pre-loaded with a builtin configuration, which is selected on startup if no configuration name is specified. This builtin configuration is equivalent to the following:
<cloud_discovery_service name="rti.cds.builtin.config.default">
<transport>
<element>
<alias>builtin.UDPv4</alias>
<receive_port>7400</receive_port>
</element>
</transport>
<domain_list>
<allow_domain_id>DOMAIN_LIST_ALL</allow_domain_id>
</domain_list>
<forwarder>
<thread_pool>
<size>2</size>
</thread_pool>
</forwarder>
<database>
<cleanup_period>
<sec>50</sec>
</cleanup_period>
</database>
</cloud_discovery_service>
The builtin configuration has the name rti.cds.builtin.config.default,
which is reserved; no additional configurations can have this name.
6.4. Overriding XML Settings¶
Cloud Discovery Service allows you to override certain XML settings through the use of the command-line options. When these options are explicitly specified, their values will override the values of the equivalent XML elements.
See Command-Line Options for a list of the available options that can override XML settings.