Chapter 2 Introduction
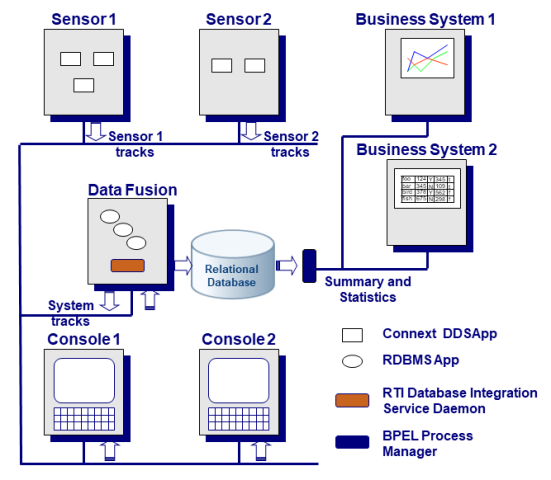
In this section, a few of the unique qualities and features of Database Integration Service are discussed in greater detail. Figure 2.1: Example System Using Database Integration Service shows an example system where Database Integration Service serves as the central integration technology to interconnect the real-time, embedded world with the analysis and high-level decision-making processes of the enterprise world.
In Figure 2.1: Example System Using Database Integration Service, sensors of physical processes produce data that must be filtered, fused, and stored for use in business processes. In addition, multiple user consoles must have concurrent access to both raw and fused data.
Database Integration Service is the bridge that connects real-time/high performance to complex analysis, edge devices to business systems, and embedded to enterprise.
Figure 2.1: Example System Using Database Integration Service
2.1 Interconnecting Standards
Until recently, distributed real-time systems were built using custom-developed data structures and algorithms to store and manipulate data in combination with a commercial, or even proprietary, data-distribution middleware layer. This was necessary to meet real-time performance requirements. However, in recent years, DDS, a standard for data distribution, has emerged as the premier method to integrate and build distributed real-time systems.
For decades in enterprise systems, standards for communications, data representation and data storage has enabled the tremendous growth of software applications for business processes worldwide. The standards such as SQL, ODBC, JMS, HTML, XML, and WDSL have greatly increased the interoperability of those business systems.
Database Integration Service is the first commercial product that interconnects the DDS standard newly established in the embedded world to the common standards of the enterprise world. With Database Integration Service, enterprise applications have direct access to real-time data, and real-time applications have access to the plethora of processes and logic that has been developed to configure and direct actions based on business decisions.
2.2 Connectivity To Edge Devices
For edge devices, such as sensors and hand-helds, Database Integration Service integrates Connext applications with databases. Applications can publish data into relational databases and subscribe to changes in relational databases using the standard Connext application programming interface. Integration between Connext and relational database applications is supported by an IDL-to-SQL mapping that allows both types of applications to access a uniform data model.
2.3 Flexibility and Scalability
By leveraging Connext Quality-of-Service (QoS) settings, Database Integration Service supports an unprecedented variety of deployment configurations to accommodate a wide range of scenarios, from reliable point-to-point delivery to best-effort multicasting that enables real-time transaction streaming to large numbers of subscribers. By setting QoS policies, system throughput, response time, reliability, footprint, and network bandwidth consumption can be tuned to meet application requirements. Previously, a system was hard-coded with parameters set for a specific operation profile during integration. In contrast, Database Integration Service provides run-time configurable policy settings, which greatly enhances system deployment flexibility.
2.4 High Availability
Availability is an essential requirement for most distributed real-time applications. Systems built in the Defense and Aerospace industries are typically safety critical and are required to operate in crisis situations. In telecommunications, a minute of system downtime may mean many millions of dollars in lost revenue. With Database Integration Service, automatic data caching and replication can serve as the foundation technology for high-availability. Applications can use Database Integration Service to maintain copies of SQL database tables on two or more hosts in the network. In the event of a host failure, copies of the tables are available from other hosts to continue operation.
Database Integration Service’s automated replication management and no-single-point-of-failure guarantees the availability of critical information. With Database Integration Service, tables can be stored on multiple hosts, allowing applications and services to concurrently read and write in multiple tables. Conflict resolution can be based on application-defined timestamps.
2.5 Additional Benefits of Database Integration Service
- Achieve quick time-to-market
- Start application development immediately using well-known interfaces.
- Minimize time-consuming custom programming.
- Easily integrate into existing solutions using industry- standard interfaces.
- Reduce development costs
- Use widely available modeling and database tools.
- Eliminate expensive complex coding for real-time data management and communication.
- Integrate edge devices, distributed real-time data management, and enterprise databases using a single set of standard Application Programming Interfaces.
- Deliver cutting-edge solutions
- Process massive amounts of information across networks in real-time.
- Turn near-instantaneous responses to (remote) critical events into a business advantage.
- Seamlessly integrate networked applications, services, and devices.
- Minimize operational costs
- Maintain complex networked applications with near-zero administration.
- Dynamically add or change system components.
- Run on common hardware platforms and networks.
- Reduce risks
- Guarantee continuous system availability through dynamic replication management.
- Rely on continuous high-quality technical support.
- Build on years of experience in the world’s most demanding real-time application domains.