1. DDS-XRCE¶
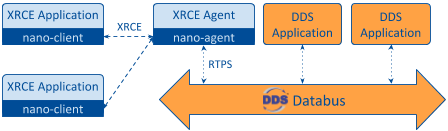
Figure 1.1 DDS-XRCE System Architecture¶
Thanks to XRCE, limited devices such as microcontrollers and other embedded targets can become part of a DDS system.
DDS-XRCE (or “DDS for eXtremely Resource Constrained Environments”) introduces an alternative interface to DDS which offloads all management of DDS entities from applications to an external Agent process.
Applications connect to the XRCE Agent as clients, and they use the XRCE Client API to:
Create and configure DDS entities on the Agent.
Write DDS samples using a DataWriter on the Agent.
Read DDS samples received by a DataReader on the Agent.
XRCE’s client/server model significantly reduces the memory footprint and network bandwidth required by an application to use DDS.
The XRCE protocol may be carried over any transport that has a Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of at least 24 bytes. There are standard mappings for TCP/UDP sockets, and Serial Transports.
The XRCE standard also defines a reliability protocol for reliable delivery of messages over unreliable transports. XRCE also supports fragmentation (and reconstruction) of large data payloads, allowing XRCE to send data larger than the transport’s MTU.