RTI Perftest
Overview
RTI Perftest is a command-line tool for measuring the minimum latency, maximum throughput, and loaded latency in a configurable set of scenarios. It can help you answer questions such as:
For a given publishing configuration (e.g., queue size, batching settings), sample size, and subscribing configuration (e.g., queue size, Listener vs. WaitSet), what is the throughput of my network?
When my network is heavily loaded, what latency can I expect?
For a given configuration, what is the best-case latency with no other traffic on the network?
RTI Perftest works by making the publishing side of the test write data as fast as it can. Every few samples (configured through the command line), RTI Perftest sends a special sample requesting an echo from the subscribing side. RTI Perftest uses this ping -> pong exchange to measure the round-trip time (RTT) for latency. From the RTT, it calculates the one-way latency time (RTT/2).
The Perftest Publisher prints the latency test results, and the Perftest Subscriber prints the throughput results.
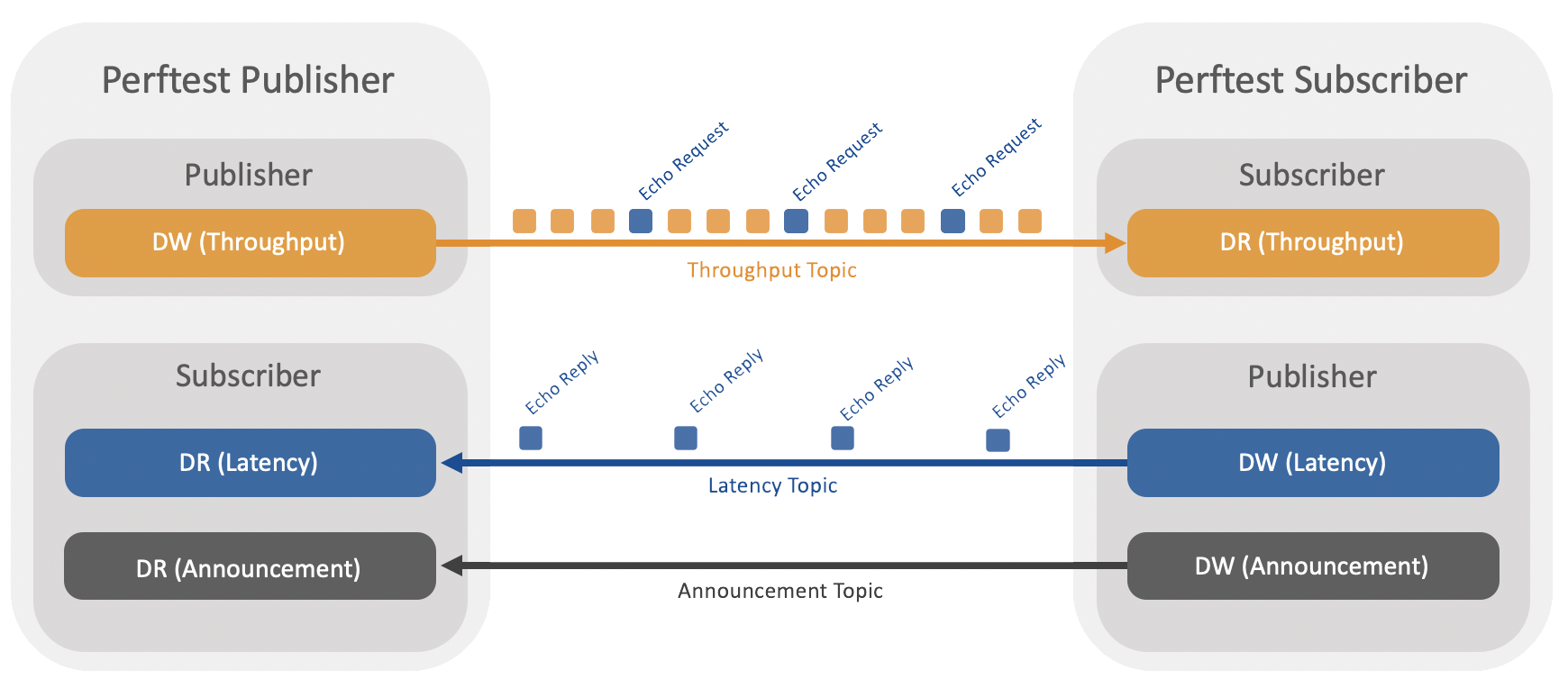
RTI Perftest allows two operational modes: Throughput Test and Latency Test.
Learn more in the Introduction section.
Features
RTI Perftest supports the following functionality:
RTI Connext DDS Professional and RTI Connext DDS Micro. Perftest also supports RTI Connext TSS over RTI Connext DDS Professional or over RTI Connext DDS Micro.
Multiple platforms, including Windows®, Linux®, macOS®, VxWorks®, and Android™.
Multiple test setups: multicast, one-to-many communication (Pub -> Sub), latency test, throughput test, and latency vs. throughput test.
Raw transports (UDPv4 sockets and shared memory segments).
Benchmarking of RTI Connext DDS Professional and RTI Connext DDS Micro features such as FlatData™ language binding and Zero Copy transfer over shared memory.
Getting Started QuickGuide
To get a local copy of your project up and running quickly, follow these simple example steps.
Download
Get the RTI Perftest bundle in one of three different ways:
Clone and compile from the official Github repository:
git clone https://github.com/rticommunity/rtiperftest.gitDownload and compile from: https://github.com/rticommunity/rtiperftest.
Download the executables for popular platforms from the binaries section in the RTI Perftest release page here.
To learn more about the supported platforms and installation, please refer to the more detailed Download section.
Prerequisites
If you need to compile RTI Perftest, there are a few prerequisites; however, if you downloaded the executables already compiled, you can skip these steps:
RTI Connext DDS Professional or RTI Connext DDS Micro should be installed in the system where the
build.shscript is going to run. The target libraries for the platform to be generated should also be installed.The
$NDDSHOMEenvironment variable should be set correctly. Or, pass$NDDSHOMEdirectly to thebuild.shscript by using the--nddshome <PATH>command-line option.If you intend to compile and test using RTI Security Plugins, you will need to link against the OpenSSL/wolfSSL libraries for your architecture.
Learn more in the Compilation section.
Compile
For Linux, macOS, QNX, VxWorks, Lynx, and Android, RTI Perftest makes use of a
script in the top-level directory named build.sh. On Windows, it uses an equivalent
script named build.bat. To build using these scripts, simply invoke them with the
command-line parameters desired.
For example, for a given architecture (x64Darwin15clang7.0), for C++ (traditional
and modern) and Java, the command would be:
./build.sh --platform x64Darwin15clang7.0
If you want to build the C# API implementation:
./build.sh --cs-build
Learn more about compilation for other platforms and examples in the Compilation section.
Usage QuickGuide
The following two examples show how to run the performance test for two use cases. Find more examples in Use-Cases and Examples.
The tests below print final results only; if you want to see intermediate values, remove the
-noprintargument from the command line.If you are running on two unequal machines—that is, one machine is faster (has better processors) than the other—you will see better performance by running the publisher on the slower machine.
Example 1: 1-to-1, Unicast, Best Latency as a Function of Message Size
Publisher:
bin/<arch>/release/perftest_cpp -pub -noPrint -nic <ipaddr> -dataLen <length> -latencyTest -executionTime 100
Subscriber:
bin/<arch>/release/perftest_cpp -sub -noPrint -nic <ipaddr> -domain <ID> -multicast
Modify -dataLen <bytes> to see latencies for different data sizes. Set
-executionTime <seconds> to be >=100 for statistically better results.
Example 2: 1-to-1, Multicast, Maximum Throughput as a Function of Message Size (with Batching)
Publisher:
bin/<arch>/release/perftest_cpp -pub -noPrint -nic <ipaddr> -dataLen <length> -batchSize <bytes> -multicast -executionTime 100
Subscriber:
bin/<arch>/release/perftest_cpp -sub -noprint -nic <ipaddr> -multicast
To achieve maximum throughput, start by setting -batchSize <bytes> to 8192,
then increase the size to see if you get better throughput.
Note
Batching will not be enabled if the data length is larger than half the batch size.
Explore the documentation for more information.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Download
- 3. Compilation
- 4. Execution
- 5. Command-Line Parameters
- 5.1. Test Parameters for Publishing and Subscribing Applications
- 5.2. Transport-Specific Options
- 5.3. Test Parameters only for Publishing Applications
- 5.4. Test Parameters only for Subscribing Applications
- 5.5. Test Parameters to Control Connext DDS Secure Options
- 5.6. Raw Transport Options
- 5.7. Additional Information about Parameters
- 6. Use-Cases and Examples
- 7. Tutorials
- 8. Optimizing Your OS For Network Performance
- 9. Extending RTI Perftest to Other Middlewares
- 10. Compatibility
- 11. Release Notes