Defines generic classes and macros to support user data types. More...
Data Structures | |
| struct | DDS_TypeAllocationParams_t |
| Configures whether or not to allocate pointer and optional members. More... | |
| struct | DDS_TypeDeallocationParams_t |
| Configures whether to release or not pointer and optional members. More... | |
| struct | Foo |
| A representative user-defined data type. More... | |
| struct | FooTypeSupport |
| <<interface>> <<generic>> User data type specific interface. More... | |
| struct | DDS_InstanceHandleSeq |
Instantiates FooSeq < DDS_InstanceHandle_t > . More... | |
Macros | |
| #define | DDS_TYPESUPPORT_C(TTypeSupport, TData) |
| Declares the interface required to support a user data type. More... | |
| #define | DDS_DATAWRITER_C(TDataWriter, TData) |
| Declares the interface required to support a user data type specific data writer. More... | |
| #define | DDS_DATAREADER_C(TDataReader, TDataSeq, TData) |
| Declares the interface required to support a user data type-specific data reader. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef DDS_HANDLE_TYPE_NATIVE | DDS_InstanceHandle_t |
| Type definition for an instance handle. More... | |
| typedef struct DDS_TypeSupportImpl | DDS_TypeSupport |
| <<interface>> An abstract marker interface that has to be specialized for each concrete user data type that will be used by the application. More... | |
Functions | |
| Foo * | FooTypeSupport_create_data (void) |
| <<extension>> Create a data type and initialize it. More... | |
| Foo * | FooTypeSupport_create_data_ex (DDS_Boolean allocatePointers) |
| <<extension>> Create a data type and initialize it. More... | |
| Foo * | FooTypeSupport_create_data_w_params (const struct DDS_TypeAllocationParams_t *alloc_params) |
| <<extension>> Create a data type and initialize it. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_copy_data (Foo *dst_data, const Foo *src_data) |
| <<extension>> Copy data type. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_delete_data (Foo *a_data) |
| <<extension>> Destroy a user data type instance. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_delete_data_ex (Foo *a_data, DDS_Boolean deletePointers) |
| <<extension>> Destroy a user data type instance. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_delete_data_w_params (Foo *a_data, const struct DDS_TypeDeallocationParams_t *dealloc_params) |
| <<extension>> Destroy a user data type instance. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_initialize_data (Foo *a_data) |
| <<extension>> Initialize data type. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_initialize_data_ex (Foo *a_data, DDS_Boolean allocatePointers) |
| <<extension>> Initialize data type. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_finalize_data (Foo *a_data) |
| <<extension>> Finalize data type. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_finalize_data_ex (Foo *a_data, DDS_Boolean deletePointers) |
| <<extension>> Finalize data type. More... | |
| const char * | FooTypeSupport_get_type_name (void) |
| Get the default name for this type. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_register_type (DDS_DomainParticipant *participant, const char *type_name) |
| Allows an application to communicate to RTI Connext the existence of a data type. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_unregister_type (DDS_DomainParticipant *participant, const char *type_name) |
| <<extension>> Allows an application to unregister a data type from RTI Connext. After calling unregister_type, no further communication using that type is possible. More... | |
| void | FooTypeSupport_print_data (Foo *a_data) |
| <<extension>> Print value of data type to standard out. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer (char *buffer, unsigned int *length, const Foo *a_data) |
| <<extension>> Serializes the input sample into a CDR buffer of octets. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer_ex (char *buffer, unsigned int *length, const Foo *a_data, DDS_DataRepresentationId_t representation) |
| <<extension>> Serializes the input sample into a buffer of octets. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_deserialize_data_from_cdr_buffer (Foo *sample, const char *buffer, unsigned int length) |
| <<extension>> Deserializes a sample from a buffer of octets. More... | |
| DDS_ReturnCode_t | FooTypeSupport_data_to_string (Foo *sample, char *str, DDS_UnsignedLong *str_size, const DDS_PrintFormatProperty *property) |
| <<extension>> Transforms a data sample into a human-readable string representation. More... | |
| DDS_TypeCode * | FooTypeSupport_get_typecode (void) |
| <<extension>> Retrieves the TypeCode for the Type. More... | |
| DDS_Boolean | DDS_InstanceHandle_equals (const DDS_InstanceHandle_t *self, const DDS_InstanceHandle_t *other) |
| Compares this instance handle with another handle for equality. More... | |
| int | DDS_InstanceHandle_compare (const DDS_InstanceHandle_t *self, const DDS_InstanceHandle_t *other) |
| Compares this instance handle with another handle. More... | |
| void | DDS_InstanceHandle_copy (DDS_InstanceHandle_t *self, const DDS_InstanceHandle_t *other) |
| Copies this instance handle into another handle. More... | |
| DDS_Boolean | DDS_InstanceHandle_is_nil (const DDS_InstanceHandle_t *self) |
| Compare this handle to DDS_HANDLE_NIL. More... | |
Variables | |
| const DDS_InstanceHandle_t | DDS_HANDLE_NIL |
| The NIL instance handle. More... | |
Detailed Description
Defines generic classes and macros to support user data types.
DDS specifies strongly typed interfaces to read and write user data. For each data class defined by the application, there is a number of specialised classes that are required to facilitate the type-safe interaction of the application with RTI Connext.
RTI Connext provides an automatic means to generate all these type-specific classes with the rtiddsgen utility. The complete set of automatic classes created for a hypothetical user data type named Foo are shown below.
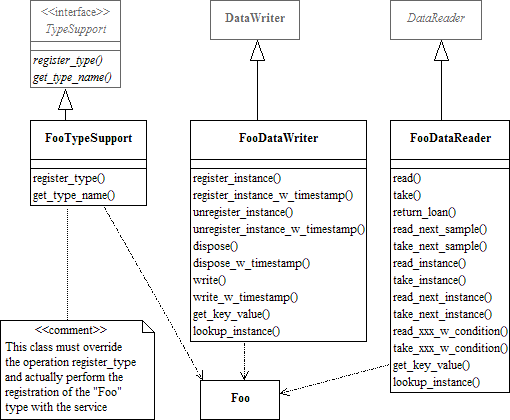
an application data type named Foo"
The macros defined here declare the strongly typed APIs needed to support an arbitrary user defined data of type Foo.
- See also
- the Code Generator User's Manual
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ DDS_TYPESUPPORT_C
| #define DDS_TYPESUPPORT_C | ( | TTypeSupport, | |
| TData | |||
| ) |
Declares the interface required to support a user data type.
- Defines:
- FooTypeSupport TypeSupport of type
Foo, i.e.FooTypeSupport
- Examples
- HelloWorldSupport.c.
◆ DDS_DATAWRITER_C
| #define DDS_DATAWRITER_C | ( | TDataWriter, | |
| TData | |||
| ) |
Declares the interface required to support a user data type specific data writer.
- Uses:
- FooTypeSupport user data type,
Foo
- Defines:
- FooDataWriter DDS_DataWriter of type
Foo, i.e.FooDataWriter
◆ DDS_DATAREADER_C
| #define DDS_DATAREADER_C | ( | TDataReader, | |
| TDataSeq, | |||
| TData | |||
| ) |
Declares the interface required to support a user data type-specific data reader.
- Uses:
- FooTypeSupport user data type,
Foo
FooSeq sequence of user data type,sequence<::Foo>
- Defines:
- FooDataReader DDS_DataReader of type
Foo, i.e.FooDataReader
- See also
- FooSeq
- Examples
- HelloWorldSupport.c.
Typedef Documentation
◆ DDS_InstanceHandle_t
| typedef DDS_HANDLE_TYPE_NATIVE DDS_InstanceHandle_t |
Type definition for an instance handle.
Handle to identify different instances of the same DDS_Topic of a certain type.
◆ DDS_TypeSupport
| typedef struct DDS_TypeSupportImpl DDS_TypeSupport |
<<interface>> An abstract marker interface that has to be specialized for each concrete user data type that will be used by the application.
The implementation provides an automatic means to generate a type-specific class, FooTypeSupport, from a description of the type in IDL.
A DDS_TypeSupport must be registered using the FooTypeSupport_register_type operation on this type-specific class before it can be used to create DDS_Topic objects.
- See also
- FooTypeSupport
- the Code Generator User's Manual
Function Documentation
◆ FooTypeSupport_create_data()
| Foo * FooTypeSupport_create_data | ( | void | ) |
<<extension>> Create a data type and initialize it.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to instantiate a data type and initialize it properly.
By default all memory for the type is deeply allocated, except for optional members.
- Returns
- Newly created data type, or NULL on failure.
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_delete_data
◆ FooTypeSupport_create_data_ex()
| Foo * FooTypeSupport_create_data_ex | ( | DDS_Boolean | allocatePointers | ) |
<<extension>> Create a data type and initialize it.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to instantiate a data type and initialize it properly.
When allocatePointers is DDS_BOOLEAN_TRUE, all the references (pointers) in the type are recursively allocated.
- Parameters
-
allocatePointers <<in>> Whether or not to recursively allocate pointers.
- Returns
- Newly created data type, or NULL on failure.
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_delete_data_ex
◆ FooTypeSupport_create_data_w_params()
| Foo * FooTypeSupport_create_data_w_params | ( | const struct DDS_TypeAllocationParams_t * | alloc_params | ) |
<<extension>> Create a data type and initialize it.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to instantiate a data type and initialize it properly.
By default all memory for the type is deeply allocated, except for optional members.
- Parameters
-
alloc_params <<in>> Whether or not to recursively allocate pointers and/or optional members
- Returns
- Newly created data type, or NULL on failure.
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_delete_data_ex
◆ FooTypeSupport_copy_data()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_copy_data | ( | Foo * | dst_data, |
| const Foo * | src_data | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Copy data type.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to copy value of a data type.
- Parameters
-
dst_data <<inout>> Data type to copy value to. Cannot be NULL. src_data <<in>> Data type to copy value from. Cannot be NULL.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
◆ FooTypeSupport_delete_data()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_delete_data | ( | Foo * | a_data | ) |
<<extension>> Destroy a user data type instance.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to destroy a data type and return all resources.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<in>> Cannot be NULL.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_create_data
◆ FooTypeSupport_delete_data_ex()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_delete_data_ex | ( | Foo * | a_data, |
| DDS_Boolean | deletePointers | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Destroy a user data type instance.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to destroy a data type and return all resources.
When deletePointers is DDS_BOOLEAN_TRUE, all the references (pointers) are destroyed as well.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_create_data_ex
◆ FooTypeSupport_delete_data_w_params()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_delete_data_w_params | ( | Foo * | a_data, |
| const struct DDS_TypeDeallocationParams_t * | dealloc_params | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Destroy a user data type instance.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to destroy a data type and return all resources.
By default, all non-NULL pointers and optional members are deleted.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<in>> Cannot be NULL. dealloc_params <<in>> Whether or not to destroy pointers and/or optional members.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_create_data_ex
◆ FooTypeSupport_initialize_data()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_initialize_data | ( | Foo * | a_data | ) |
<<extension>> Initialize data type.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to initialize a data type. This function is typically called to initialize a data type that is allocated on the stack. Calling this function more than once will cause a memory leak.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<inout>> Cannot be NULL.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_finalize_data
◆ FooTypeSupport_initialize_data_ex()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_initialize_data_ex | ( | Foo * | a_data, |
| DDS_Boolean | allocatePointers | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Initialize data type.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to initialize a data type. This function is typically called to initialize a data type that is allocated on the stack. Calling this function more than once will cause a memory leak.
When allocatePointers is DDS_BOOLEAN_TRUE, all the references (pointers) in the type are recursively allocated.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<inout>> Cannot be NULL. allocatePointers <<in>> Whether or not to recursively allocate pointers.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_finalize_data_ex
◆ FooTypeSupport_finalize_data()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_finalize_data | ( | Foo * | a_data | ) |
<<extension>> Finalize data type.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to finalize a data type. This function is typically called to finalize a data type that has previouslly been initialized.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<in>> Cannot be NULL.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_initialize_data
◆ FooTypeSupport_finalize_data_ex()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_finalize_data_ex | ( | Foo * | a_data, |
| DDS_Boolean | deletePointers | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Finalize data type.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to finalize a data type. This function is typically called to finalize a data type that has previouslly been initialized.
When deletePointers is DDS_BOOLEAN_TRUE, the memory required by the references (pointers) associated to the type is freed.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<in>> Cannot be NULL. deletePointers <<in>> Whether or not to free memory allocated by the pointers.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
◆ FooTypeSupport_get_type_name()
| const char * FooTypeSupport_get_type_name | ( | void | ) |
Get the default name for this type.
Can be used for calling FooTypeSupport_register_type or creating DDS_Topic
- Returns
- default name for this type
◆ FooTypeSupport_register_type()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_register_type | ( | DDS_DomainParticipant * | participant, |
| const char * | type_name | ||
| ) |
Allows an application to communicate to RTI Connext the existence of a data type.
The generated implementation of the operation embeds all the knowledge that has to be communicated to the middleware in order to make it able to manage the contents of data of that type. This includes in particular the key definition that will allow RTI Connext to distinguish different instances of the same type.
The same DDS_TypeSupport can be registered multiple times with a DDS_DomainParticipant using the same or different values for the type_name. If register_type is called multiple times on the same DDS_TypeSupport with the same DDS_DomainParticipant and type_name, the second (and subsequent) registrations are ignored but the operation returns DDS_RETCODE_OK.
- Precondition
- Cannot use the same
type_nameto register two different DDS_TypeSupport with the same DDS_DomainParticipant, or else the operation will fail and DDS_RETCODE_PRECONDITION_NOT_MET will be returned.
- Parameters
-
participant <<in>> the DDS_DomainParticipant to register the data type Foowith. Cannot be NULL.type_name <<in>> the type name under with the data type Foois registered with the participant; this type name is used when creating a new DDS_Topic. (See DDS_DomainParticipant_create_topic.) The name may not be NULL or longer than 255 characters.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes, DDS_RETCODE_PRECONDITION_NOT_MET or DDS_RETCODE_OUT_OF_RESOURCES.
- MT Safety:
- UNSAFE on the FIRST call. It is not safe for two threads to simultaneously make the first call to register a type. Subsequent calls are thread safe.
◆ FooTypeSupport_unregister_type()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_unregister_type | ( | DDS_DomainParticipant * | participant, |
| const char * | type_name | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Allows an application to unregister a data type from RTI Connext. After calling unregister_type, no further communication using that type is possible.
The generated implementation of the operation removes all the information about a type from RTI Connext. No further communication using that type is possible.
- Precondition
- A type with
type_nameis registered with the participant and all DDS_Topic objects referencing the type have been destroyed. If any DDS_Topic is associated with the type, the operation will fail with DDS_RETCODE_ERROR.
- Postcondition
- All information about the type is removed from RTI Connext. No further communication using this type is possible.
- Parameters
-
participant <<in>> the DDS_DomainParticipant to unregister the data type Foofrom. Cannot be NULL.type_name <<in>> the type name under with the data type Foois registered with the participant. The name should match a name that has been previously used to register a type with the participant. Cannot be NULL.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes, DDS_RETCODE_BAD_PARAMETER or DDS_RETCODE_ERROR
- MT Safety:
- SAFE.
- See also
- FooTypeSupport_register_type
◆ FooTypeSupport_print_data()
| void FooTypeSupport_print_data | ( | Foo * | a_data | ) |
<<extension>> Print value of data type to standard out.
The generated implementation of the operation knows how to print value of a data type.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<in>> Data type to be printed.
◆ FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer | ( | char * | buffer, |
| unsigned int * | length, | ||
| const Foo * | a_data | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Serializes the input sample into a CDR buffer of octets.
This function serializes a sample into a buffer of octets and it uses CDR as the data representation. Calling this function is equivalent to calling FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer_ex with DDS_AUTO_DATA_REPRESENTATION as the representation.
The input buffer must be big enough to store the serialized representation of the sample. Otherwise, the function will return an error.
To determine the minimum size of the input buffer, the user must call this method with the buffer set to NULL.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<in>>. Input sample. Cannot be NULL. buffer <<out>>. Serialization buffer. length <<inout>>. When bufferis set to NULL, after the function executes,lengthwill contain a buffer size big enough to hold the serialized data. Whenbufferis not NULL,lengthmust contain the size of the input buffer when the function is invoked. After the function executes,lengthwill be updated to contain the actual size of the serialized content, which may be smaller than the size obtained whenbufferis set to NULL.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
◆ FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer_ex()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer_ex | ( | char * | buffer, |
| unsigned int * | length, | ||
| const Foo * | a_data, | ||
| DDS_DataRepresentationId_t | representation | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Serializes the input sample into a buffer of octets.
This function serializes a sample into a buffer of octets using the input data representation. See FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer for details.
- Parameters
-
a_data <<in>>. Input sample. Cannot be NULL. buffer <<out>>. Serialization buffer. length <<inout>>. Serialization buffer length. representation <<in>>. Representation used to serialize the data.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
◆ FooTypeSupport_deserialize_data_from_cdr_buffer()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_deserialize_data_from_cdr_buffer | ( | Foo * | sample, |
| const char * | buffer, | ||
| unsigned int | length | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Deserializes a sample from a buffer of octets.
This function deserializes a sample from a CDR buffer of octets.
The content of the buffer generated by the function FooTypeSupport_serialize_data_to_cdr_buffer can be provided to this function to get the sample back.
- Parameters
-
sample <<in>>. Output sample. Cannot be NULL. buffer <<in>>. Deserialization buffer. Cannot be NULL. length <<in>>. Length of the serialized representation of the sample in the buffer.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes
◆ FooTypeSupport_data_to_string()
| DDS_ReturnCode_t FooTypeSupport_data_to_string | ( | Foo * | sample, |
| char * | str, | ||
| DDS_UnsignedLong * | str_size, | ||
| const DDS_PrintFormatProperty * | property | ||
| ) |
<<extension>> Transforms a data sample into a human-readable string representation.
This function takes a data sample and creates a string representation of the data.
The input character buffer must be big enough to store the string representation of the sample. Otherwise, the function will return an error.
To determine the minimum size of the input character buffer, the user must call this method with the buffer set to NULL.
If the size of the output string is longer than the size of an unsigned 32-bit integer, this operation will fail with DDS_RETCODE_OUT_OF_RESOURCES.
This method is only provided for types that were generated with typecodes.
- Parameters
-
sample <<in>>. The sample to get the string representation for. Cannot be NULL. str <<out>>. Output string representing the data sample. str_size <<inout>>. When stris set to NULL, after the function executes,str_sizewill contain a buffer size big enough to hold the string representation of the data. Whenstris not NULL,str_sizemust contain the size of the input buffer when the function is invoked. If the size of the input buffer is too small, after the function executes,str_sizewill be updated to contain the required size of the string content and the function will return DDS_RETCODE_OUT_OF_RESOURCES.property <<in>>. Properties describing what the format of the output string should be.
- Returns
- One of the Standard Return Codes, DDS_RETCODE_OUT_OF_RESOURCES
◆ FooTypeSupport_get_typecode()
| DDS_TypeCode * FooTypeSupport_get_typecode | ( | void | ) |
<<extension>> Retrieves the TypeCode for the Type.
This function retrieves the DDS_TypeCode for the Type. A DDS_TypeCode is a mechanism for representing a type at runtime. RTI Connext can use type codes to send type definitions on the network. A DDS_TypeCode value consists of a type code kind (represented by the DDS_TCKind enumeration) and a list of members (that is, fields). These members are recursive: each one has its own DDS_TypeCode, and in the case of complex types (structures, arrays, and so on), these contained type codes contain their own members.
- Returns
- The TypeCode for this type
◆ DDS_InstanceHandle_equals()
| DDS_Boolean DDS_InstanceHandle_equals | ( | const DDS_InstanceHandle_t * | self, |
| const DDS_InstanceHandle_t * | other | ||
| ) |
Compares this instance handle with another handle for equality.
- Parameters
-
self <<in>> This handle. Cannot be NULL. other <<in>> The other handle to be compared with this handle. Cannot be NULL.
- Returns
- DDS_BOOLEAN_TRUE if the two handles have equal values, or DDS_BOOLEAN_FALSE otherwise.
- See also
- DDS_InstanceHandle_is_nil
◆ DDS_InstanceHandle_compare()
| int DDS_InstanceHandle_compare | ( | const DDS_InstanceHandle_t * | self, |
| const DDS_InstanceHandle_t * | other | ||
| ) |
Compares this instance handle with another handle.
- Parameters
-
self <<in>> This handle. Cannot be NULL. other <<in>> The other handle to be compared with this handle. Cannot be NULL.
- Returns
- If the two handles are equal, the function returns 0. If self is greater than other the function returns a positive number; otherwise, it returns a negative number.
- See also
- DDS_InstanceHandle_is_nil
◆ DDS_InstanceHandle_copy()
| void DDS_InstanceHandle_copy | ( | DDS_InstanceHandle_t * | self, |
| const DDS_InstanceHandle_t * | other | ||
| ) |
◆ DDS_InstanceHandle_is_nil()
| DDS_Boolean DDS_InstanceHandle_is_nil | ( | const DDS_InstanceHandle_t * | self | ) |
Compare this handle to DDS_HANDLE_NIL.
- Returns
- DDS_BOOLEAN_TRUE if the given instance handle is equal to DDS_HANDLE_NIL or DDS_BOOLEAN_FALSE otherwise.
- See also
- DDS_InstanceHandle_equals
Variable Documentation
◆ DDS_HANDLE_NIL
|
extern |
The NIL instance handle.
Special DDS_InstanceHandle_t value
- See also
- DDS_InstanceHandle_is_nil
- Examples
- HelloWorld_publisher.c.