1. Before You Get Started
1.1. What is Connext?
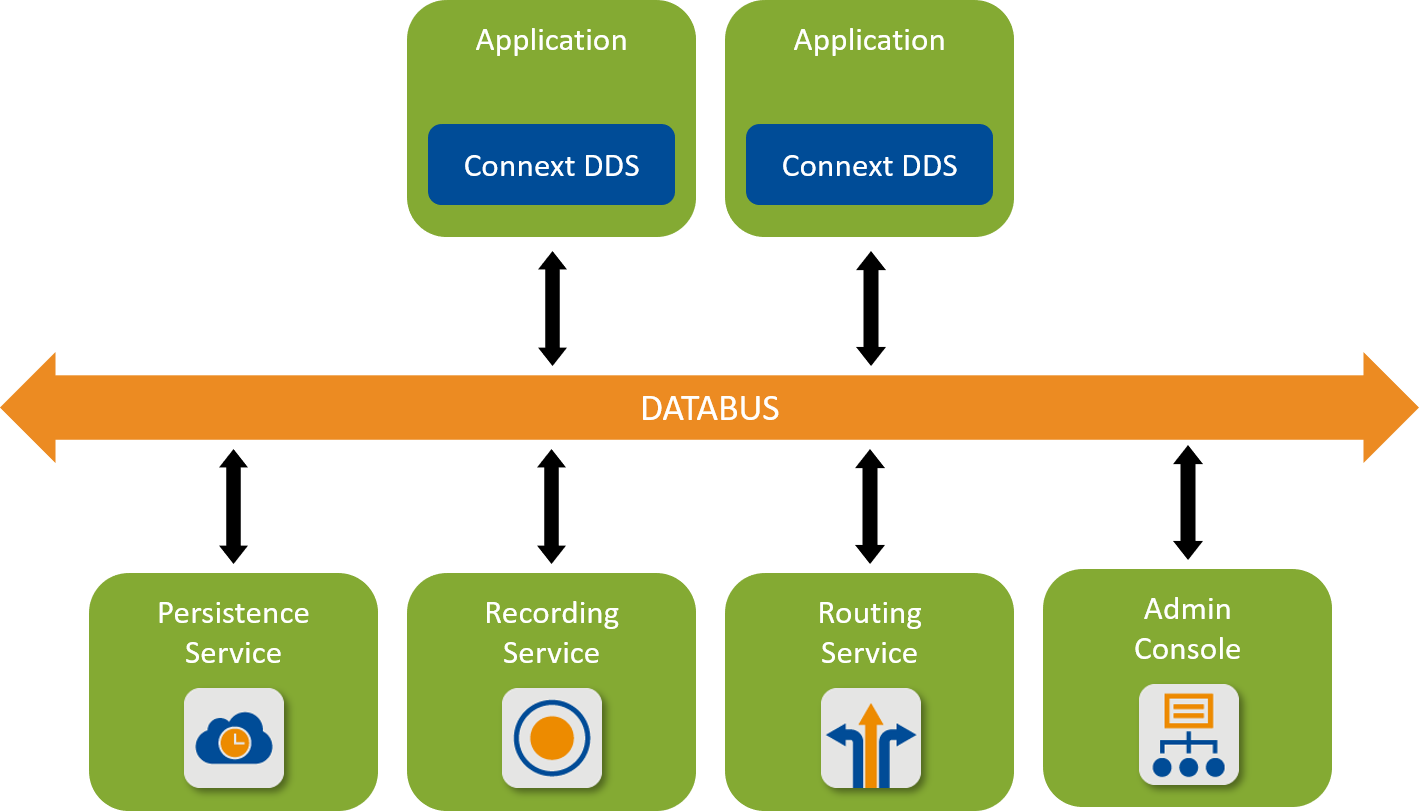
RTI® Connext® DDS is a connectivity framework for building distributed applications with requirements for high performance and scalability. It includes these components:
An SDK that provides you with APIs to help you send and receive data using the communication patterns described in this documentation (see Next Steps). These APIs allow you to connect your own applications to other applications on the databus.
Tools that help you visualize your data and debug your distributed system.
Infrastructure Services that can perform dedicated functions in your system, such as recording, bridging, and persisting data.
1.2. Downloading Connext
If you haven’t already purchased a Connext bundle, you can follow this Getting Started guide with an evaluation bundle. To obtain an evaluation bundle, click the Free Trial button at https://www.rti.com/. Fill out the brief form, and you will receive an evaluation package shortly.
1.3. Installing Connext
To develop Python applications, you will need the following Connext bundles:
A host bundle that contains files such as documentation, the code generator, other tools, and infrastructure services executables. The host bundle is provided in a .run or .exe file that will run an installer.
Host bundles are named:
rti_connext_dds-<version>-<package_type>-host-<host-platform>.runrti_connext_dds-<version>-<package_type>-host-<host-platform>.dmgrti_connext_dds-<version>-<package_type>-host-<host-platform>.exeThe
<package_type>is usuallypro.The
<host_platform>depends on your development platform, such asx64Win64for a 64-bit Windows® platform.
The Python API, required to develop Connext Python applications. The Python API is supported on Python 3.6 to 3.12, and on Linux® x64, Windows® x64, and macOS® x64 and arm64.
There are two ways to install it:
Install it from pypi.org. This installation method requires a license file when you run your application (see Setting up a License for the Python API).
$ pip install rti.connext
or
Install it from your host installation directory. This method doesn’t require a license file.
$ pip install rti.connext.activated -f <installdir>/resource/python_api
Note that pypi.org package allows writing Python applications without a host installation, but this guide uses the code generator and some tool that are included in the host package.
If you plan to develop C, C++, or Java applications or use add-on libraries you will also need a target bundle. See the C++ version of this Getting Started Guide for more information.
1.3.1. Installing a Host
The host bundle is an application; thus, it can be started from a GUI or command line. To install the host bundle, do either of the following:
Double-click the installer.
Run the installation script from a command prompt. See Installing RTI Connext, in the RTI Connext Installation Guide.
1.3.2. Installing additional packages with a GUI
After you install the host bundle, you’ll have a tool called RTI Launcher. (See Starting Launcher, in the RTI Launcher User’s Manual.)
To install additional packages from the Launcher tool, open the Configuration tab, and select “Install RTI Packages.” This will open a dialog that allows you to select one or more .rtipkg files that you would like to install.
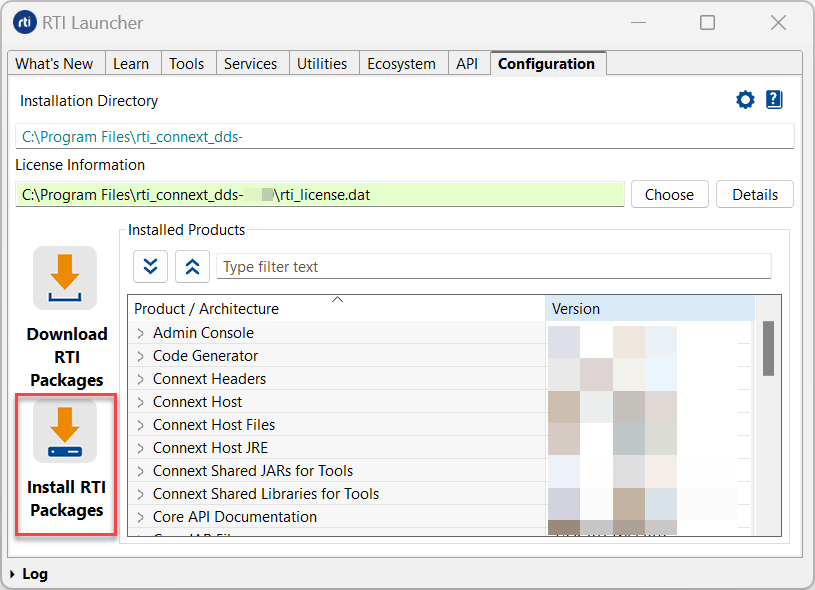
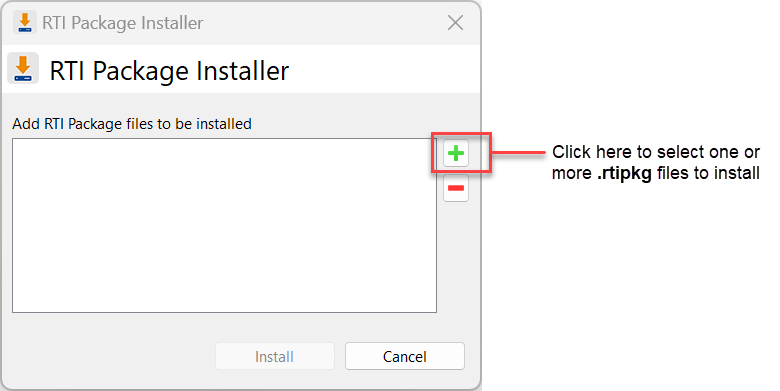
1.3.3. Installing additional packages from a Command Line
To install additional packages from the command line, type:
$ <installdir>/bin/rtipkginstall <path to rtipkg>
$ <installdir>/bin/rtipkginstall <path to rtipkg>
> <installdir>\bin\rtipkginstall <path to rtipkg>
1.3.4. Paths Mentioned in Documentation
This documentation refers to the following directories, depending on your operating system:
$NDDSHOME This refers to the installation directory for Connext.
The default installation paths are:
Non-root user:
/home/<your user name>/rti_connext_dds-<version>Root user:
/opt/rti_connext_dds-<version>
$NDDSHOME is an environment variable set to the installation path.
$NDDSHOME This refers to the installation directory for Connext.
The default installation path is:
/Applications/rti_connext_dds-<version>
$NDDSHOME is an environment variable set to the installation path.
%NDDSHOME% This refers to the installation directory for Connext.
The default installation paths are:
User without Administrator privileges:
<your home directory>\rti_connext_dds-<version>User with Administrator privileges:
"C:\Program Files\rti_connext_dds-<version>"
%NDDSHOME% is an environment variable set to the installation path.
Note
When using a command prompt to enter a command that includes the path
C:\Program Files (or any directory name that has a space), enclose
the path in quotation marks. For example:
“C:\Program Files\rti_connext_dds-version\bin\rtilauncher.bat”.
Or if you have defined the NDDSHOME environment variable:
"%NDDSHOME%\bin\rtilauncher.bat".
Sometimes this documentation uses <NDDSHOME> to refer to the installation path.
Whenever you see <NDDSHOME> used in a path, replace it with $NDDSHOME for Linux or
macOS systems, with %NDDSHOME% for Windows systems, or with your installation path.
1.4. Setting Up a License
1.4.1. Setting up a License for the Python API
If you’re using the rti.connext.activated package, you don’t need a license file
to run your applications.
If you’re using the package from pypi.org, rti.connext, your applications
need to load a license file every time they run. To obtain an evaluation license,
click the Free Trial button at https://www.rti.com/.
There are several ways to specify your license file:
You can copy the rti_license.dat file to the location where you run your application.
You can set the
RTI_LICENSE_FILEenvironment variable to the full path of your license file, including the file name.You can set the
DomainParticipantQosto point to your license file (see the License Management section in the RTI Connext Installation Guide).
1.4.2. Setting up a License for the tools and other features
Most installations require a license file to run the tools or features included in the Connext platform. If your distribution requires a license file, you will receive one from RTI via e-mail.
The easiest way to permanently configure your license file is using Launcher, as shown below:
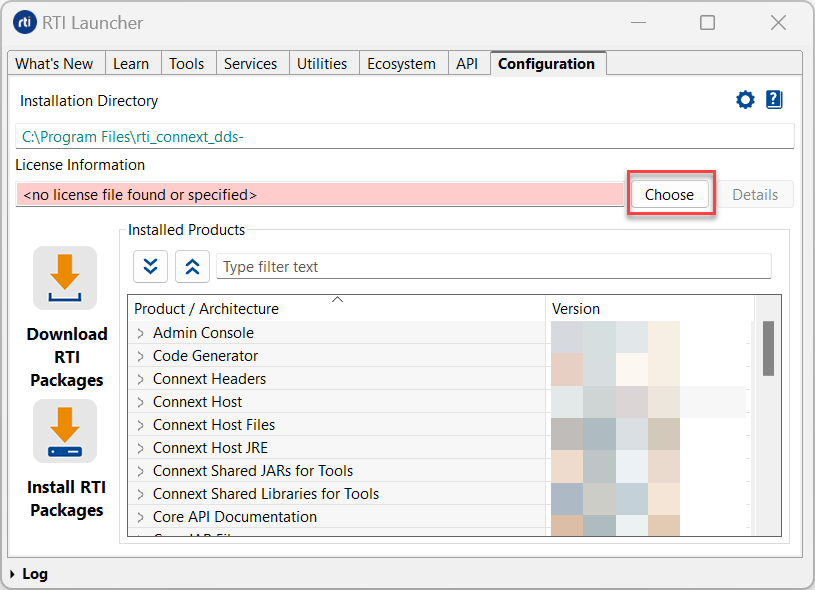
If you do not want to use Launcher, you can also install a license by placing it in one of these two locations:
<installation directory>/rti_license.dat<workspace directory>/rti_license.dat
The workspace directory is in this location by default, depending on your operating system:
/home/<your username>/rti_workspace/
/Users/<your username>/rti_workspace/
<your Windows documents folder>\rti_workspace\
A third way to install a license is to configure the environment
variable RTI_LICENSE_FILE to point to your license file.
For more details on how to install a license file, see the License Management section in the RTI Connext Installation Guide.
1.5. Checking What is Installed
To find out what target libraries or add-ons you have installed, you can use the Launcher tool. See Starting Launcher, in the RTI Launcher User’s Manual. Once in Launcher, open the Configuration tab.
To check your Python API installation, run:
$ pip show rti.connext
or
$ pip show rti.connext.activated
1.6. Troubleshooting the Python API Installation
1.6.1. resource/python_api under Connext installation directory doesn’t exist
Make sure you have installed a host package. The evaluation installers
don’t include rti.connext.activated. If you have an evaluation
installer, install rti.connext (using the first method described
in Installing Connext) and make sure your evaluation license file is
accessible, for example by copying rti_license.dat to the current directory,
where you launch your Python application.
1.6.2. pip install fails with ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement rti.connext
If you get this error while installing the Python API with pip install, you
may have to upgrade pip:
$ pip install --upgrade pip
If the installation still fails after that, make sure your Python version is supported (see Installing Connext).
1.6.3. pip install fails because I don’t have permissions to install packages
You can use a virtual environment to install packages without requiring admin privileges. To create a virtual environment, run the following commands:
$ python -m venv myvenv
$ . myvenv/bin/activate
$ pip install rti.connext
$ python -m venv myvenv
$ . myvenv/bin/activate
$ pip install rti.connext
> python -m venv myvenv
> myvenv\Scripts\activate.bat
> pip install rti.connext
For more information about installing Python packages with pip, see the Python documentation: Virtual Environments and Packages.
1.6.4. I get “No module named ‘rti’” when I run my Python application
Make sure you have installed the Python API for your current Python interpreter and/or virtual environment (see Checking What is Installed).
If you still get that or a similar error, try reinstalling it by adding
--force-reinstall to the pip install command.
1.7. Where Do I Get More Help?
The full RTI Connext DDS Installation Guide contains more information:
Installer command-line options
Controlling the location of the RTI Workspace directory
Additional license management options
Special backup of RTI libraries
How to uninstall Connext
Additional documentation and user forums can be found on community.rti.com.
Continue to Publish/Subscribe to start learning about the capabilities and features of Connext.