|
RTI Connext DDS Micro C++ API
Version 3.0.3
|
|
RTI Connext DDS Micro C++ API
Version 3.0.3
|
Modules | |
| DomainParticipantFactoryQos | |
| DomainParticipantQos | |
| DataReaderQos | |
| DataWriterQos | |
| OSAPI | |
| UDP Transport | |
| Dynamic Participant Static Endpoint (DPSE) | |
| Dynamic Participant Dynamic Endpoint (DPDE) | |
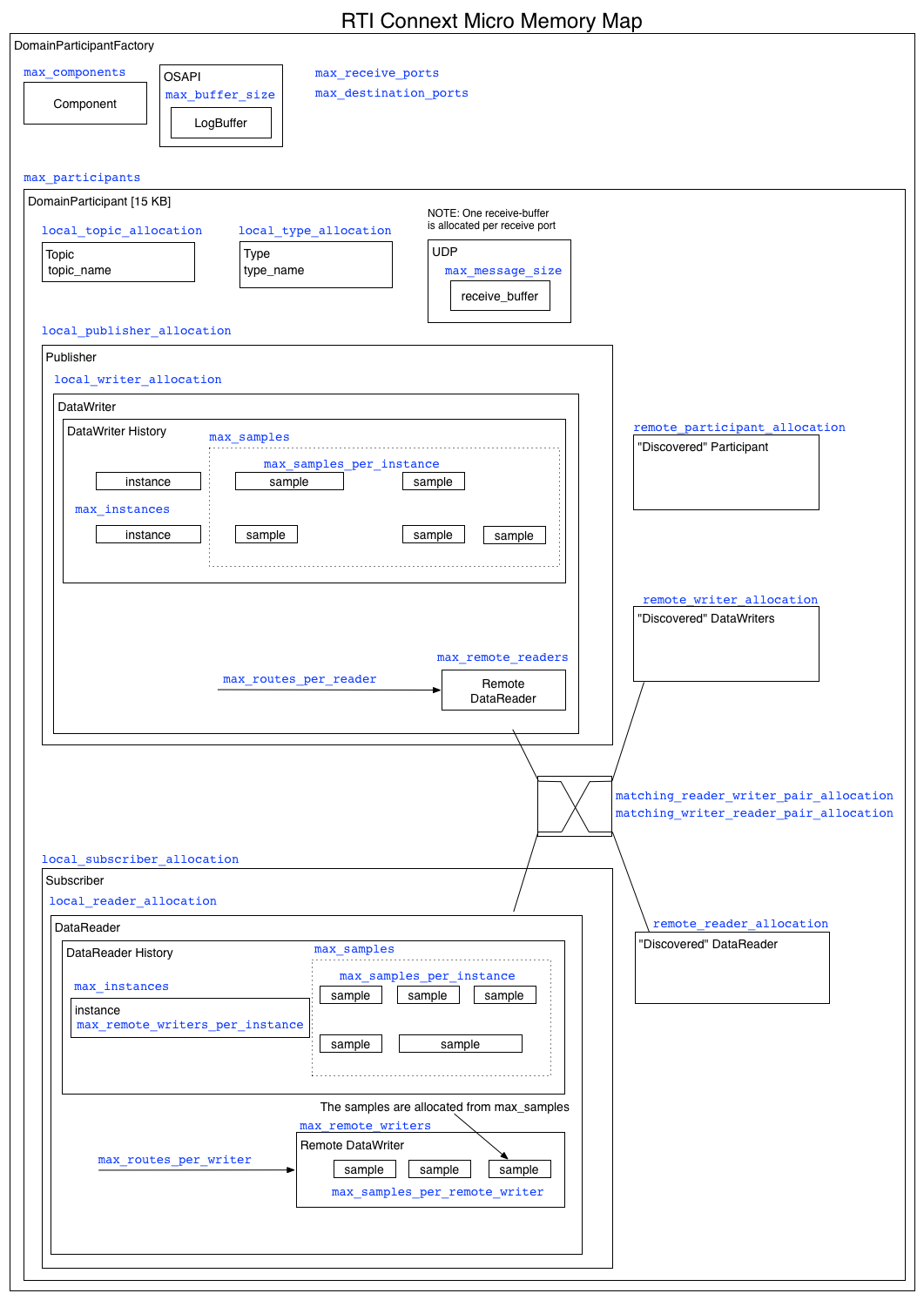
RTI Connext DDS Micro is designed for use in real-time systems and uses a predictable and deterministic memory manager to ensure that memory growth is not unbounded, OS memory fragmentation is eliminated and memory usage can be determined a-priori. The advantage with this design is that proper operation is ensured as soon as steady state has been reached. However, it also places an additional burden on the system designer to properly configure each resource-limit. This section describes all the resource limits in RTI Connext DDS Micro and how they impact RTI Connext DDS Micro’s behavior and memory usage.
RTI Connext DDS Micro allocates heap memory to create internal data-structures. It is important to know that RTI Connext DDS Micro manages memory allocated from the system heap using its own internal memory management, and only returns memory allocated from the system back to the system when something is deleted. That is, if an application never deletes anything, no memory is returned to the system.
As a rule of thumb, in RTI Connext DDS Micro only APIs that end in _create() or _new() allocate heap memory and APIs that end in _delete() or _free() frees memory. An exception to this rule is dynamic discovery which allocates memory at run-time for the topic and type names.
RTI Connext DDS Micro does not support dynamically allocating resources beyond the initial configuration. That is, all resource limits must be finite. This restriction may be removed in a future version.
All resource-limits in RTI Connext DDS Micro is specified in a Qos policy or property. The figure below illustrates where the various resource-limits are applied, and the following sections describe each user adjustable resource-limit in more detail. All numbers in blue corresponds to a resource-limit.