4.1. Introduction¶
This section provides platform-specific instructions that you will need to build and run RTI Connext Micro applications.
For each supported operating system (OS), this section describes:
Supported combinations of OS versions, CPUs, and compilers
How to build your application, including:
Required Connext Micro and system libraries
Required compiler and linker flags
Details on how the Connext Micro libraries were built
To see a list of all supported platforms, refer to Supported Platforms and Programming Languages.
4.1.1. Library types¶
Connext Micro provides precompiled binaries for supported architectures. This section explains the different library types and gives a general description of the binaries shipped by RTI.
In this section, the following terms are used:
toolchain refers to the compiler, linker, and archiver for a specific CPU architecture, excluding dependencies in standard header files and libraries.
platform refers to the hardware, BSPs, OS kernel, and C/C++ libraries that are not included in the toolchain (such as
libc,libc++, and the network stack).
RTI builds two types of binaries for Connext Micro: integrated libraries and split libraries. RTI may include either or both types of binaries for a given target architecture.
4.1.1.1. Integrated libraries¶
All Connext Micro target packages include a core library called rti_me. The rti_me
library includes all the required basic functionality for Connext Micro.
The term “integrated library” refers to an rti_me library where all the OS
integration and network stack integration is compiled directly into rti_me.
This means that it is not possible to change how the OS and network integration
has been written without recompiling the entire library. This is illustrated below:
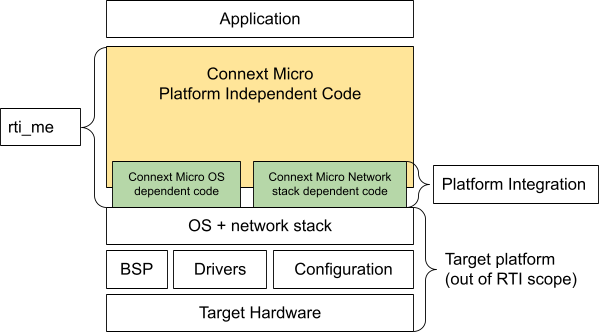
Figure 4.1 An overview of rti_me as an integrated library¶
Note
All binaries provided for Connext Micro version 4.0.1 and below are integrated libraries.
4.1.1.2. Split libraries¶
In contrast to an integrated library, split libraries consist of a Platform Independent Library (PIL) and a Platform Support Library (PSL).
The PIL is an rti_me library that includes all functionality for
Connext Micro except for platform integration code.
The PSL consists of two libraries that support OS integration and network stack integration:
The OS Platform Support Library (
ospsl): Contains the required OS support, such as mutex and semaphore support. This library is very limited in functionality.The Network Support Library (
netiopsl): Includes support for transports, such as UDPv4.
The ospsl and netiopsl libraries are collectively referred to as the
PSL (even though it is more than one library).
This is illustrated below:
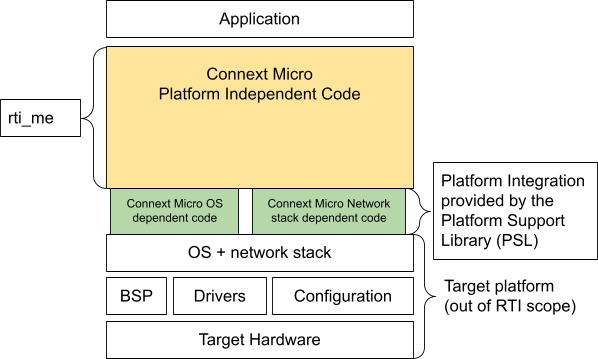
Figure 4.2 An overview of split libraries¶
The main benefit of split libraries is that different PSLs can be written for the same PIL without having to recompile the platform-independent code.
Note
The PIL is compiled without standard C header files and is only dependent on the toolchain. This is different from the integrated libraries, which are compiled with standard C header files.
The PSL is always compiled against the standard C header files, as well as other platform-dependent header files.
4.1.2. Library descriptions¶
The following libraries are included in the target bundle. Note that the names listed below do not include platform-specific prefixes or suffixes.
Depending on the target architecture, the library name is prefixed with lib and the library suffix also varies between target architectures, such as .so and .dylib.
The following naming conventions are also used:
Static libraries have a z suffix.
Shared libraries do not have an additional suffix.
Debug libraries have a d suffix.
Release libraries do not have an additional suffix.
For example:
rti_mezdindicates a static debug library.rti_meindicates a dynamically linked release library.
Library Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The core library, including the DDS C API. |
|
The Dynamic Participant Static Endpoint (DPSE) plugin. |
|
The Dynamic Participant Dynamic Endpoint (DPDE) plugin. |
|
The Reader History plugin. |
|
The Writer History plugin. |
|
The Zero Copy v1 over shared memory transport library plugin. |
|
The Shared Memory Transport plugin. |
|
The Application Generation plugin. |
|
The C++ API. |
|
The OS PSL. |
|
The C NETIO PSL. |
|
The C++ NETIO PSL library. |
|
The Zero Copy v2 transport library plugin (not supported on all platforms). |
|
The content filtering library. |
|
The X-Types library. |
|
The Lightweight Security Plugin PIL (installed separately, not supported on all platforms). |
|
The Lightweight Security Plugin Transform PSL (installed separately, not supported on all platforms). |
4.1.3. Build profiles¶
You can optionally build Connext Micro with a CERT profile. This restricts Connext Micro to only include features that are available or planned for Connext Cert; for more information, see Building Connext Micro with Compatibility for Connext Cert.
Any architecture ending with CERT is built with the CERT profile enabled.
Some features are only available on specific platforms; see the footnotes in the table below.
Feature/Capability |
Non-CERT Profile |
CERT Profile |
|---|---|---|
Dynamic Participant Discovery |
✓ |
✓ |
Static Endpoint Discovery |
✓ |
✓ |
Dynamic Endpoint Discovery |
✓ |
|
C++ API |
✓ |
|
Shared Memory Transport (SHMEM) |
✓ 1 |
|
Zero Copy v1 |
✓ 1 |
|
Zero Copy v2 |
||
Micro Application Generator (MAG) |
✓ |
|
Content Filtering |
✓ |
|
Lightweight Security Plugin |
✓ 3 |
✓ 3 |
X-Types |
✓ |
4.1.4. Supported libraries by platform¶
The following table shows which Connext Micro libraries are supported on each platform (RTI architecture).
Platform |
RTI Architecture |
Supported Libraries |
|---|---|---|
Windows 10 x64 |
x86_64lePEvs2017 |
|
x86_64lePEvs2017CERT |
|
|
macOS 14 x64 |
x86_64leMachOclang15.0 |
|
x86_64leMachOclang15.0CERT |
|
|
macOS 14 arm64 |
armv8leMachOclang15.0 |
|
armv8leMachOclang15.0CERT |
|
|
Ubuntu 22.04 x64 |
x86_64leElfgcc12.3.0 |
|
x86_64leElfgcc12.3.0CERT |
|
|
Ubuntu 18.04 ARMv8 |
armv8leElfgcc7.3.0 |
|
armv8leElfgcc7.3.0CERT |
|
|
Yocto 5.15.96 |
armv8aleElfgcc11.3.1 |
|
armv8aleElfgcc11.3.1CERT |
|
|
QNX 7.1 ARMv8 |
armv8leElfqnx_qcc8.3.0 |
|
armv8leElfqnx_qcc8.3.0CERT |
|
|
QOS 2.2.1 (QNX OS for Safety) |
armv8leElfqcc8.3.0 |
|
armv8leElfqcc8.3.0CERT |
|
|
FreeRTOS 10.0.0 ARMv7E-M |
armv7emleElfgcc10.3.1 |
|
armv7emleElfgcc10.3.1CERT |
|
4.1.5. Supported transports by platform¶
The following table shows which transports are supported on each architecture.
Platform |
RTI Architecture |
Intra |
UDPv4 |
SHMEM |
Zero Copy v1 |
Zero Copy v2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Windows 10 x64 |
x86_64lePEvs2017 |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
x86_64lePEvs2017CERT |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
macOS 14 x64 |
x86_64leMachOclang15.0 |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
x86_64leMachOclang15.0CERT |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
macOS 14 arm64 |
armv8leMachOclang15.0 |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
armv8leMachOclang15.0CERT |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
Ubuntu 22.04 x64 |
x86_64leElfgcc12.3.0 |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
x86_64leElfgcc12.3.0CERT |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|||
Ubuntu 18.04 ARMv8 |
armv8leElfgcc7.3.0 |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
armv8leElfgcc7.3.0CERT |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|||
Auto Yocto Linux BSP 37.0 |
armv8aleElfgcc11.3.1 |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
armv8aleElfgcc11.3.1CERT |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|||
QNX 7.1 ARMv8 |
armv8leElfqnx_qcc8.3.0 |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
armv8leElfqnx_qcc8.3.0CERT |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|||
QOS 2.2.1 (QNX OS for Safety) |
armv8leElfqcc8.3.0 |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
armv8leElfqcc8.3.0CERT |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|||
FreeRTOS 10.4.6 ARMv7E-M |
armv7emleElfgcc10.3.1 |
✓ |
✓ |
|||
armv7emleElfgcc10.3.1CERT |
✓ |
✓ |